
Some of us can hardly be separated from a cup of coffee in the morning or evening. Caffeine fills our days and helps us stay awake, even though in fact we are very tired and need rest.
But you may not realize that coffee drinking habits have a real impact on the brain. From reduced memory performance to the risk of age-related cognitive decline. This substance can change the way of thinking of our brain in a way that is arguably interesting.
Caffeine does not actually provide energy to our body at all. This substance only affects the brain to think that our body is not tired. By replacing the substance called adenosine, we don't feel sleepy at all
Adenosine is a substance produced by the brain as a signal that our body is exhausted and needs rest. The more these substances gather in our brain, the more we feel tired and sleepy.
Then how can caffeine replace the adenosine?
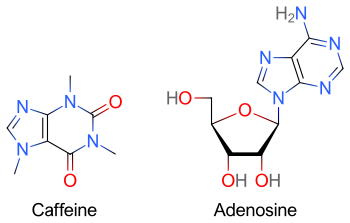
When we consume a cup of coffee or a glass of soda, caffeine will flow with blood to the brain. Because of its similar structure, the magic receptor chooses caffeine because it is lighter than adenosine. So that we don't feel sleepy and tired again.
Basically this substance only replaces the position of adenosine. So that the brain gradually begins to slow down the signal, which results in an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. Of course something that rises in the end must go down.
The receptor finally releases caffeine, and allows adonesin to re-enter. So that we also begin to feel back feeling tired and sleepy. 6 hours after consuming coffee or soda, we will only feel half of the effect.
The next morning, we will begin to feel sleepy again all caused by adonesin which is still active. That's the result that we have to feel, after consuming a cup of coffee.
 Some of us can hardly be separated from a cup of coffee in the morning or evening. Caffeine fills our days and helps us stay awake, even though in fact we are very tired and need rest.
But you may not realize that coffee drinking habits have a real impact on the brain. From reduced memory performance to the risk of age-related cognitive decline. This substance can change the way of thinking of our brain in a way that is arguably interesting.
Caffeine does not actually provide energy to our body at all. This substance only affects the brain to think that our body is not tired. By replacing the substance called adenosine, we don't feel sleepy at all
Adenosine is a substance produced by the brain as a signal that our body is exhausted and needs rest. The more these substances gather in our brain, the more we feel tired and sleepy.
Some of us can hardly be separated from a cup of coffee in the morning or evening. Caffeine fills our days and helps us stay awake, even though in fact we are very tired and need rest.
But you may not realize that coffee drinking habits have a real impact on the brain. From reduced memory performance to the risk of age-related cognitive decline. This substance can change the way of thinking of our brain in a way that is arguably interesting.
Caffeine does not actually provide energy to our body at all. This substance only affects the brain to think that our body is not tired. By replacing the substance called adenosine, we don't feel sleepy at all
Adenosine is a substance produced by the brain as a signal that our body is exhausted and needs rest. The more these substances gather in our brain, the more we feel tired and sleepy.
 When we consume a cup of coffee or a glass of soda, caffeine will flow with blood to the brain. Because of its similar structure, the magic receptor chooses caffeine because it is lighter than adenosine. So that we don't feel sleepy and tired again.
Basically this substance only replaces the position of adenosine. So that the brain gradually begins to slow down the signal, which results in an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. Of course something that rises in the end must go down.
The receptor finally releases caffeine, and allows adonesin to re-enter. So that we also begin to feel back feeling tired and sleepy. 6 hours after consuming coffee or soda, we will only feel half of the effect.
The next morning, we will begin to feel sleepy again all caused by adonesin which is still active. That's the result that we have to feel, after consuming a cup of coffee.
When we consume a cup of coffee or a glass of soda, caffeine will flow with blood to the brain. Because of its similar structure, the magic receptor chooses caffeine because it is lighter than adenosine. So that we don't feel sleepy and tired again.
Basically this substance only replaces the position of adenosine. So that the brain gradually begins to slow down the signal, which results in an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. Of course something that rises in the end must go down.
The receptor finally releases caffeine, and allows adonesin to re-enter. So that we also begin to feel back feeling tired and sleepy. 6 hours after consuming coffee or soda, we will only feel half of the effect.
The next morning, we will begin to feel sleepy again all caused by adonesin which is still active. That's the result that we have to feel, after consuming a cup of coffee.
Tinggalkan Komentar